La maladie d'Alzheimer représente la majeure partie des cas de démence et, pendant des décennies, les seuls traitements disponibles ont été des médicaments qui tentent de restaurer les niveaux de neurotransmetteurs dans le cerveau, qui n'affectent que les symptômes et ont au mieux des effets modestes. Le dernier médicament a été approuvé il y a 17 ans.
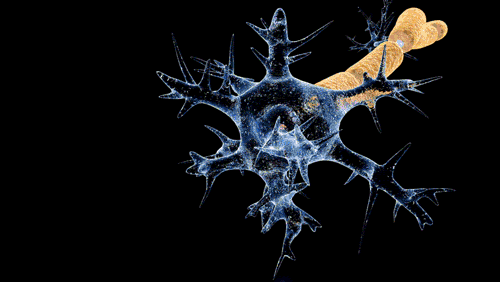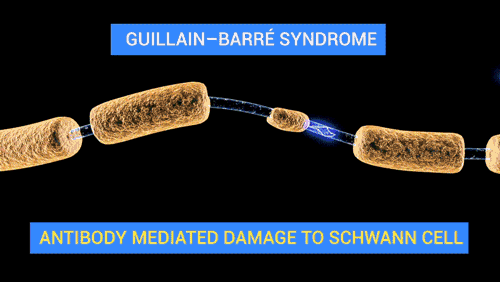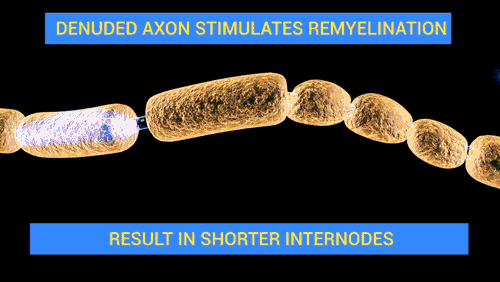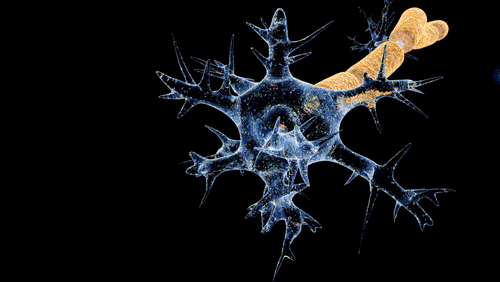
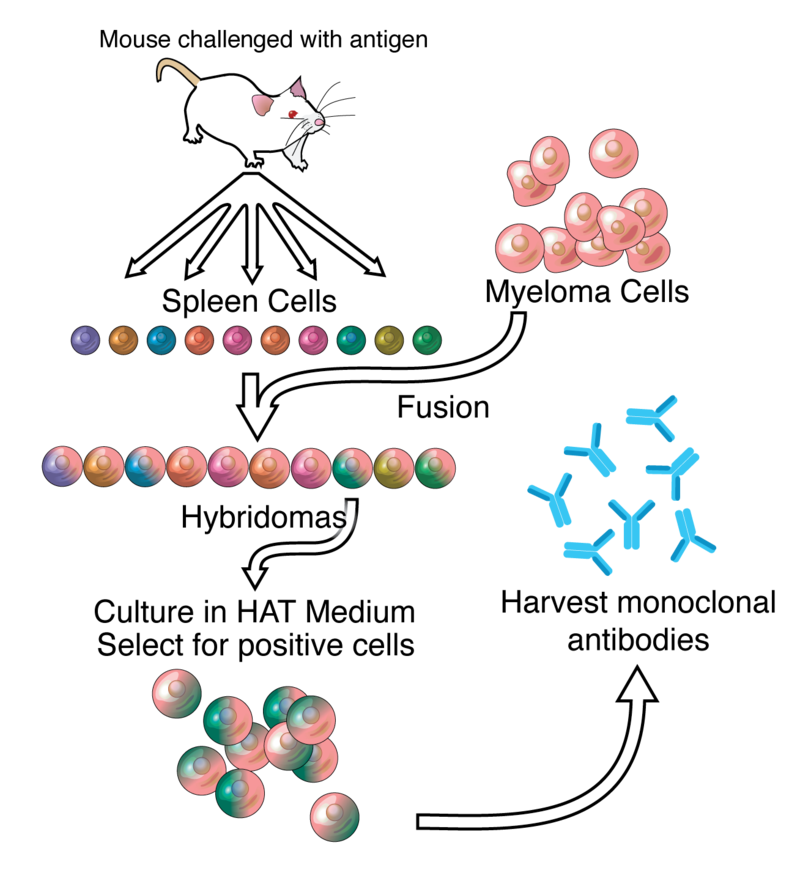 Anticorps monoclonal, source Adenosine via Wikipedia.
Anticorps monoclonal, source Adenosine via Wikipedia.
Depuis de nombreuses années, les chercheurs se sont concentrés sur les manifestations physiques de la maladie d'Alzheimer, à savoir les plaques amyloïdes extracellulaires et, plus récemment, les enchevêtrements intracellulaires de protéines tau.
Plus de 200 essais cliniques ont échoué, dont beaucoup sont passés à l'étape coûteuse des tests de phase III. Cependant l’un de ces médicaments, pourtant écarté, a été reproposé l'année dernière par Biogen et soumis à la FDA cet été 2020.
L'agence prévoit de décider du sort du traitement d'ici le 7 mars 2021. L’agrément par la FDA de l'aducanumab montrera dans quelle mesure la FDA et son commissaire, Stephen Hahn, M.D., sont prêts à s'écarter de ses normes d'approbation établies.
Le long cheminement de Biogen vers l’agrément de mise sur le marché, a été un chemin semé de revers, d'échecs qui ont été très médiatisés. Un exemple très récent concerne le neurologue de la Mayo Clinic, David Knopman, M.D., qui a été éliminé d’un comité consultatif évaluant l'aducanumab. Knopman avait, en fait, été un critique majeur du médicament.
Une société Chinoise, Green Valley, une société pharmaceutique basée à Shanghai, pourrait cependant obtenir rapidement les agréments pour les marchés Américains et Européens. Son médicament nommé Oligomannate est dérivé d'algues brunes
Aducanumab qui était sur le point d'être abandonné par Biogen et qui nécessitait de sérieuses contorsions des résultats de son essai clinique, pour lui trouver de faibles lueurs d'efficacité, a été trouvé comme «hautement convaincant» par la FDA publiés mercredi matin 5 Novembre.
Les données sous-tendant le dépôt de la FDA proviennent de deux études de phase III appelées EMERGE (alias étude 301) et ENGAGE qui ont testé l'aducanumab chez des patients atteints de la maladie d'Alzheimer précoce et légère, ainsi que d'un essai cliniquede phase 1b.
Il y avait un écart entre les études de phase III - les patients de l’essai EMERGE (alias étude 302) qui ont reçu la dose la plus élevée d’aducanumab ont présenté une amélioration statistiquement significative sur une échelle de démence clinique, mais le même groupe de patients de l’étude ENGAGE a fait pire que patients prenant un placebo sur cette même mesure, ainsi que sur un test de fonction cognitive.
De plus, le programme de phase III a raté une analyse de futilité en mars 2019, ce qui a conduit Biogen à mettre fin aux études, mais la société a fait volte-face huit mois plus tard, affirmant que l'analyse était «incorrecte».
Pour certains analystes, il s'agissait simplement de ma,ipulation de données, une astuce généralement utilisée par les biotechnologies à micro-capitalisation pour essayer d’extirper de données négatives des messages attrayants aux investisseurs. Ce n’est pas un comportement que vous associeriez à une grande biopharmacie.
Une approbation par la FDA pourrait rapporter de 5 milliards de dollars à 10 milliards de dollars de ventes de pointe à Biogen grâce à ce médicament. Selon des analystes, un lancement réussi de l'aducanumab «a le potentiel de changer complètement le profil de l'entreprise», dont la recherche a subi récemment de nombreux revers.
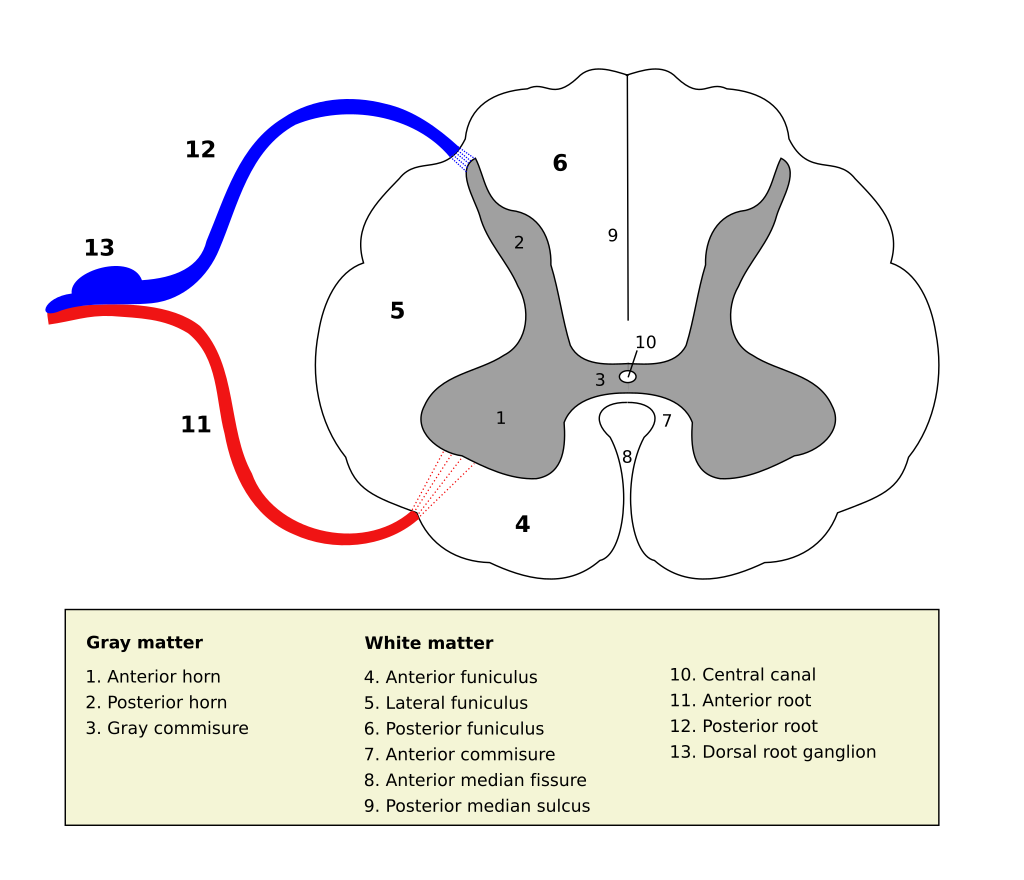 Source Wikipedia/User Polarlys
Source Wikipedia/User Polarlys


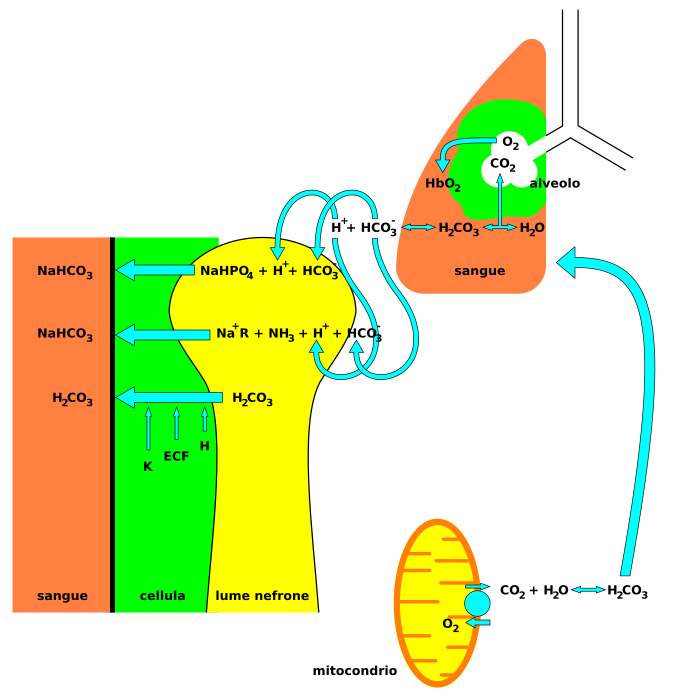 Nervous system involvement may be seen with acidosis. Signs and symptoms that may be seen in acidosis include headaches, confusion, feeling tired, tremors, sleepiness, flapping tremor, and dysfunction of the cerebrum of the brain which may progress to coma if there is no intervention.
Nervous system involvement may be seen with acidosis. Signs and symptoms that may be seen in acidosis include headaches, confusion, feeling tired, tremors, sleepiness, flapping tremor, and dysfunction of the cerebrum of the brain which may progress to coma if there is no intervention.
 Anticorps monoclonal, source Adenosine via Wikipedia.
Anticorps monoclonal, source Adenosine via Wikipedia.